Scaling
This page describes routines that deal with scaling data. The Excel form will in have the following two layouts depending on the option the user selects.
Layout A:
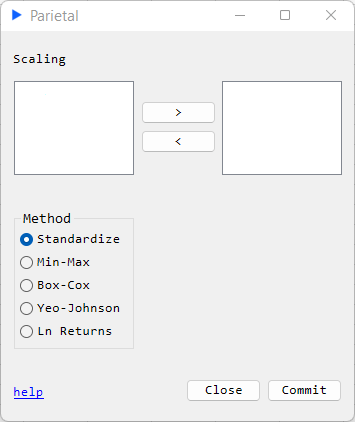
Layout B:
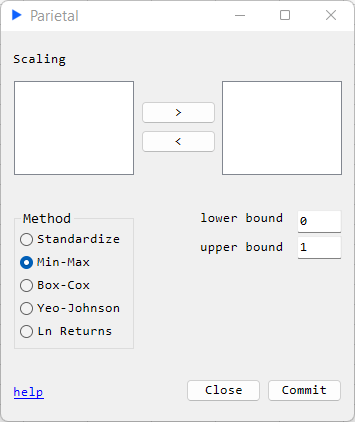
Standardize
Description
Return a matrix that is column-wise centered to mean 0 and scaled to a standard devation 1. More precisely, each original in a column corresponds to the following transformation: where is the column mean and is the column standard deviation.
Returns
- Matrix with the scaled columns
Min-Max
Description
Return a matrix that is column-wise scaled to a lower bound and an upper bound specified by the user. More precisely, each original in a column corresponds to the following transformation:
Returns
- Matrix with the scaled columns
Box-Cox
Description
Return a matrix that is column-wise scaled using the Box-Cox transform. The transform itself is defined as:
An optimization routine is used to find the parameter maximizing the log-likelihood function for the Box-Cox transform.
Returns
- for each column
- Matrix with the scaled columns
Yeo-Johnson
Description
Return a matrix that is column-wise scaled using the Yeo-Johnson transform. The transform itself is defined as:
An optimization routine is used to find the parameter maximizing the log-likelihood function for the Yeo-Johnson transform.
Returns
- for each column
- Matrix with the scaled columns
Log Returns
Description
Return a matrix that calculates column-wise natural log returns.
Returns
- Matrix